mixed numbers:
The hidden meaning
of everyday digits
Interstate Highway Codes

Highway travel was born in America in the early 1900s. As cities were connected, commerce, tourism, and communication all experienced a rapid increase. While the complexity of American infrastructure also increased, planning travel wasn't always as simple as directions from Mapquest.
According to the Federal Highway Administration, by 1925, there were nearly 300 different high-volume, long-distance roadways, each with its own system of route names and symbols. Around this time the American Association of State Highway Officials requested that the Secretary of Agriculture investigate the creation of a standardized highway system.
Almost 30 years later, Eisenhower authorized the Federal Aid Highway Act, providing standards for the reclassification and building of roads and developing the following naming system:
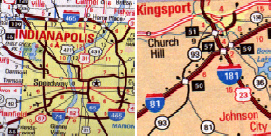
Two-digit numbers specify major routes; odd for north-south roads and even for east-west roads. North-south roads are numbered consecutively starting in the west; east-west roads are numbered consecutively south to north. Names of major cross-country routes end in 5 or 0.

Three-digit numbers refer to routes serving major two-digit routes, reflected by the last two digits in their numbers. Loops and cross-city freeways begin with an even number, routes branching off a major highway begin with an odd number.
For More Information:
© Patrick Williams 2003-2004
xhtml | CSS | 508